The windows graphics system uses pens and brushes to set the appearance of the graphic objects (lines, curves, shapes). Pens defines the style, thickness and colour of the pixels will be drawn, while a brush determines the fill colour of shapes.
The CDC object class contains member functions to perform the basic drawing functionality. For a full overview of the CDC class https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/mfc/reference/cdc-class?view=vs-2019
A sample of the graphics object functions found in the CDC class is listed below
Displaying Pixels
Single pixels can be drawn on the the screen using the member function SetPixel –
COLORREF SetPixel(int x,int y,COLORREF pColour);
COLORREF SetPixel(POINT point,COLORREF pColor);
Where
x – Specifies the logical x-coordinate.
y – Specifies the logical y-coordinate.
pColor – specifies the color used to paint the point.
point – Encapsulates a single (x,y) coordinate.
Returns an RGB value for the color that is actually painted. This value may be different from that specified by pColor if an approximation is used. If the function fails the return value is -1.
MoveToEx
The initial starting position for graphics output will be the screen coordinate position 0,0 however this can be set by the application with a call to the member function moveto(). The prototype for the moveto() function is –
CPoint MoveTo(int x,int y);
CPoint MoveTo(POINT point);
where
x – specifies the x-coordinate of the new position, in logical units.
y – specifies the y-coordinate of the new position, in logical units.
point – specifies the new position using either a point structure or a CPoint obejct.
Drawing Lines
LineTo() draws a line from the current position to a specified position and moves the current position to the end of the line –
BOOL LineTo(int x, int y);
BOOL LineTo(POINT point);
where
x – Specifies the logical x-coordinate of the new position.
y – Specifies the logical y-coordinate of the new position.
point – Encapsulates a single (x,y) coordinate.
Returns the x and y coordinates of the previous position as a CPoint object.
PolylineTo
Connects a set of points with line segments
BOOL PolylineTo(const POINT* lpPoints,int nCount);
lpPoints – Points to an array of POINT data structures that contains the vertices of the line.
nCount – Specifies the number of points in the array.
Returns nonzero if the function is successful; otherwise 0.
Ellipse
The member function Ellipse draws a circle or an ellipse
BOOL Ellipse( int x1, int y1,int x2,int y2);
BOOL Ellipse(LPCRECT lpRect);
Where
x1 – Specifies the x-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the ellipse’s bounding rectangle.
y1 – Specifies the y-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the ellipse’s bounding rectangle.
x2 – Specifies the x-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the ellipse’s bounding rectangle.
y2 – Specifies the y-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the ellipse’s bounding rectangle.
lpRect – Encapsulates the ellipse’s bounding rectangle.
Returns non zero if the function is successful; otherwise 0.
Chord
The member function Chord draws a line segment connecting two points on a curve
BOOL Chord( int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3, int y3, int x4,int y4);
BOOL Chord(LPCRECT lpRect,POINT ptStart,POINT ptEnd);
x1 – Specifies the x-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the chord’s bounding rectangle.
y1 – Specifies the y-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the chord’s bounding rectangle.
x2 – Specifies the x-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the chord’s bounding rectangle.
y2 – Specifies the y-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the chord’s bounding rectangle.
x3 – Specifies the x-coordinate of the point that defines the chord’s starting point.
y3 – Specifies the y-coordinate of the point that defines the chord’s starting point.
x4 – Specifies the x-coordinate of the point that defines the chord’s endpoint .
y4 – Specifies the y-coordinate of the point that defines the chord’s endpoint .
lpRect – Encapsulates the bounding rectangle (in logical units).
ptStart – Specifies the x- and y-coordinates of the point that defines the chord’s starting point. This point does not have to lie exactly on the chord. .
ptEnd – Specifies the x- and y-coordinates of the point that defines the chord’s ending point (in logical units). This point does not have to lie exactly on the chord.
Returns non zero if the function is successful; otherwise 0.
Pie
The member function Pie draws a pie-shaped wedge by drawing an elliptical arc whose center and two endpoints are joined by lines.
BOOL Pie( int x1, int y1,int x2, int y2,int x3, int y3,int x4, int y4);
BOOL Pie(LPCRECT lpRect,POINT ptStart,POINT ptEnd);
Where
x1 Specifies the x-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the bounding rectangle.
y1 Specifies the y-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the bounding rectangle.
x2 Specifies the x-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the bounding rectangle.
y2 Specifies the y-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the bounding rectangle.
x3 Specifies the x-coordinate of the arc’s starting point.
y3 Specifies the y-coordinate of the arc’s starting point.
x4 Specifies the x-coordinate of the arc’s endpoint (in logical units). This point does not have to lie exactly on the arc.
y4 Specifies the y-coordinate of the arc’s endpoint.
lpRect encapsulates the bounding rectangle.
ptStart Specifies the starting point of the arc.
ptEnd Specifies the endpoint of the arc.
Returns nonzero if the function is successful; otherwise 0.
Polygon
The member function Polygon() Connects a set of points to form a polygon shape
BOOL Polygon(LPPOINT lpPoints, int nCount);
Parameters
lpPoints – Points to an array of points that specifies the vertices of the polygon. Each point in the array is a POINT structure or a CPoint object.
nCount – Specifies the number of vertices in the array.
Returns non zero if the function is successful; otherwise 0.
Rectangle
The member function rectangle() draws a 4 sided shape
BOOL Rectangle(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2);
BOOL Rectangle(LPCRECT lpRect);
x1 Specifies the x-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the rectangle.
y1 Specifies the y-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the rectangle.
x2 Specifies the x-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the rectangle .
y2 Specifies the y-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the rectangle.
lpRect Specifies the rectangle in logical units. You can pass either a CRect object or a pointer to a RECT structure for this parameter.
Returns nonzero if the function is successful; otherwise 0.
RoundRect
The member function RoundRect() draws a rectangle with rounded corners
BOOL RoundRect( int x1, int y1,int x2,int y2, int x3,int y3);
BOOL RoundRect(LPCRECT lpRect, POINT point);
x1 Specifies the x-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the rectangle.
y1 Specifies the y-coordinate of the upper-left corner of the rectangle.
x2 Specifies the x-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the rectangle.
y2 Specifies the y-coordinate of the lower-right corner of the rectangle.
x3 Specifies the width of the ellipse used to draw the rounded corners.
y3 Specifies the height of the ellipse used to draw the rounded corners.
lpRect encapsulates the bounding rectangle in logical units. You can pass either a CRect object or a pointer to a RECT structure for this parameter. The x-coordinate of point specifies the width of the ellipse to draw the rounded corners. The y-coordinate of point specifies the height of the ellipse to draw the rounded corners. You can pass either a POINT structure or a CPoint object for this parameter.
Returns nonzero if the function is successful; otherwise 0.
For full details of Windows drawing capabilities use the following
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/mfc/reference/cdc-class?view=vs-2019
The following short program illustrates some of the windows line and shape drawing capabilities
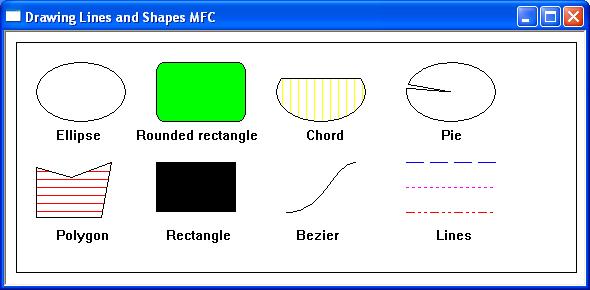
#include <afxwin.h>
class CSimpleApp : public CWinApp
{
public:
BOOL InitInstance();
};
class CMainFrame : public CFrameWnd
{
public:
CMainFrame();
DECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP()
afx_msg void OnPaint();
};
BOOL CSimpleApp::InitInstance(){
m_pMainWnd = new CMainFrame();
m_pMainWnd->ShowWindow(m_nCmdShow);
return TRUE;
}
CMainFrame::CMainFrame()
{
CRect rect(10,10,600,300);
Create(NULL, TEXT("Drawing Lines and Shapes MFC"),WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW,rect);
}
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CMainFrame,CFrameWnd)
ON_WM_PAINT()
END_MESSAGE_MAP()
CSimpleApp MFCApp1;
afx_msg void CMainFrame::OnPaint()
{
CPaintDC dc(this);
//array structure for polygon
CPoint polygon[8];
polygon[0] = CPoint(30, 185);
polygon[1] = CPoint(95, 185);
polygon[2] = CPoint(105, 130);
polygon[3] = CPoint(65, 145);
polygon[4] = CPoint(30, 135);
//array structure for bezier curve
CPoint bezier[8];
bezier[0] = CPoint(280, 180);
bezier[1] = CPoint(320, 180);
bezier[2] = CPoint(325, 130);
bezier[3] = CPoint(350, 130);
//draw bounding box for display
dc.MoveTo(10,10);
dc.LineTo(570,10);
dc.LineTo(570,240);
dc.LineTo(10,240);
dc.LineTo(10,10);
//draws ellipse using default pen and brush
dc.Ellipse(30, 30, 120, 90);
dc.TextOut(50,95,TEXT("Ellipse"),7);
//draws rounded rectangle with green brush
CBrush crColor(RGB(0, 255, 0));
dc.SelectObject(crColor);
dc.RoundRect( 150, 30, 240, 90, 15, 20);
dc.TextOut(130,95,TEXT("Rounded rectangle"),17);
//draws chord with yellow vertical hatchbrush
CBrush hatchbrush;
hatchbrush.CreateHatchBrush(HS_VERTICAL ,RGB(255,255,0));
dc.SelectObject(hatchbrush);
dc.Chord( 270, 30, 360, 90, 270, 45, 360, 45);
dc.TextOut(300,95,TEXT("Chord"),5);
//draws polygon with red horitizontal hatchbrush
CBrush hatchbrush1;
hatchbrush1.CreateHatchBrush(HS_HORIZONTAL ,RGB(255,0,0));
dc.SelectObject(hatchbrush1);
dc.Polygon(polygon, 5);
dc.TextOut(50,195,TEXT("Polygon"),7);
//draws rectangle with black brush
CBrush blackbrush(RGB(0,0,0));
dc.SelectObject(blackbrush);
dc.Rectangle( 150, 130, 230, 180);
dc.TextOut(160,195,TEXT("Rectangle"),9);
//draws Bezier curve with default pen
dc.PolyBezier(bezier,4);
dc.TextOut(290,195,TEXT("Bezier"),6);
//draws pie with white brush
CBrush whitebrush(RGB(255,255,255));
dc.SelectObject(whitebrush);
dc.Pie(400,30, 490,90, 270,45, 360,45);
dc.TextOut(435,95,TEXT("Pie"),3);
//draw lines
CPen hpen(PS_DASH,1,RGB(0, 0, 255));
dc.MoveTo(400,130);
dc.SelectObject(hpen);
dc.LineTo(490,130);
dc.MoveTo(400,155);
CPen hpen1(PS_DOT,1,RGB(255, 0, 255));
dc.SelectObject(hpen1);
dc.LineTo(490,155);
dc.MoveTo(400,180);
CPen hpen2(PS_DASHDOTDOT,1,RGB(255, 0, 0));
dc.SelectObject(hpen2);
dc.LineTo(490,180);
dc.TextOut(430,195,TEXT("Lines"),5);
}